第一节 语言学概述
1. Language语言Language is a means of verbal communication. It is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.
(1)Design Features of Language语言的本质特征

(2)Functions of language语言的功能

2. Linguistics语言学
Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language. It studies not any particular language, but languages in general.
(1)Main branches of linguistic语言学的主要分支
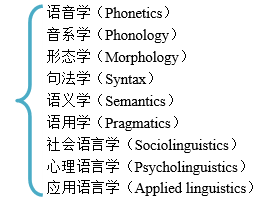
(2)语言学中的几对重要概念

第二节 语音学与音系学
1. Phonetics(1)Definition — the study of the production and perception of speech sounds.
(2)Classification
2. Phonology
It is the study of the phonemic system and sound patterning of a particular language. It studies the distinctive sound units of a language and their relationship to one another.
(1)Phonemes and allophones音位和音位变体
Phonemes — the basic unit in phonological analysis
Allophones — variants of a phoneme
(2)Minimal pair最小对比对/最小对立体
If a group of words are phonetically the same except one common position of the series of the sounds, like pet, bet, get, met, net, they are called minimal pairs.
(3)Phonological process and phonological rules
a. Phonological process音系过程
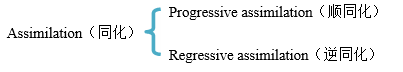
b. Phonological rules音系规则

第三节 形态学
1. Definition
It is a branch of linguistics which studies the internal structure of words, and the rules by which words are formed.
(1)Morpheme语素 — the smallest functioning unit in the composition of words
the smallest meaningful constituent unit in a language
the minimal linguistic sign
the minimal form of grammatical analysis
2. Types of Morphemes词素的类型

3. Word formation词的构成

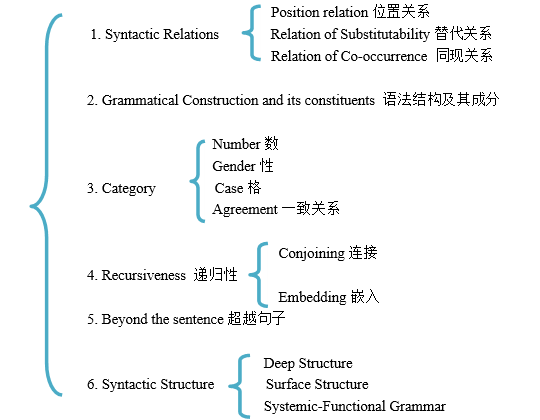
第四节 句法学